
A Website Creation or application by means of which goods or services are sold over the internet
What is Ecommerce?
Ecommerce stands for “electronic commerce.” Ecommerce websites are built to connect shoppers to products or services for trading online. On the most basic level, they provide everything we need for online shopping. They work like this:
- A business builds the website and lists the products or services they sell, along with prices. (There are a ton of ecommerce platforms or Online shopping platforms out there that make it easier to start your online business.)
- A customer finds the website, then buys goods and services. When they’ve decided they’re done online shopping, they move to the checkout phase.
- Following the website’s checkout process, the buyer provides the necessary payment and shipping information.
- The ecommerce website sends the payment information through a payment processor that validates the payment and collects the funds.
- The seller then ships the order to the customer or sends the digital product immediately via email.
How Do Ecommerce Websites Work
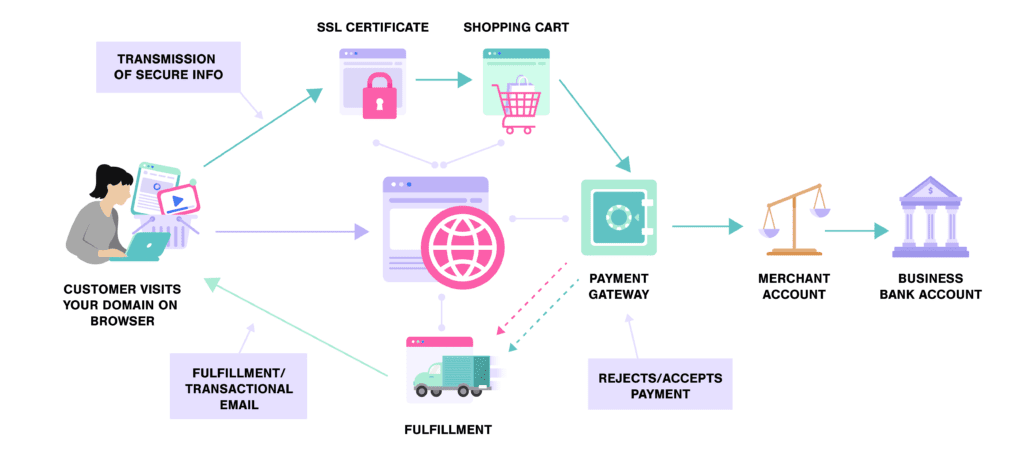
- Ecommerce Website Platform: The framework or tool your website is built with. Examples include Shopify, BigCommerce, Wix, etc.
- Shopping Cart: The part of your website that facilitates checkout and product purchase.
- SSL Certificate: The technology that keeps your website secure for financial transactions.
- Payment Gateway: The technology that accepts payment information from customers and approves or declines payment based on whether the funds are available.
- Payment Processor: The company that manages the credit card transaction – the third party between the customer and you as the merchant.
- Business Bank Account: The checking account funds go to after transactions are complete and processed through the merchant account.
- Fulfillment: The process to warehouse and ship packages to customers.
Different Types Of Ecommerce Website Hosting
- On-premise hosting means that a business keeps all the hardware and software for its website in-house – typically somewhere with the company’s physical office location. This approach is expensive because the business must purchase and maintain all the servers, firewall, operating systems, software licensing, etc. They must maintain backups and upgrades. If your company doesn’t have an IT team on staff or the money to hire one, on-premise is not a good choice for you.
- Headless ecommerce separates the front and back end of an ecommerce application. This approach provides brands with more flexibility over the customer experience. There’s more freedom to build whatever you want. Headless commerce requires using APIs, engagement tools, experience managers, and an IT team. As such, smaller businesses tend to opt for other solutions.
- Software as a service, is a popular business model. Not just for ecommerce platforms, SaaS enables businesses to get access to all the software they need without having to be tied to the machine they’re using. SaaS solutions are accessible from any device where there’s an internet connection.
When it comes to SaaS ecommerce, many popular platforms are available including Great1.com, Shopify, BigCommerce, and Wix. These solutions take care of everything for the customer. There’s no need to worry about web hosting, software licenses, domain name, SSL certificate, etc. In exchange for a monthly or annual fee, the service provider handles all of the technical stuff. It’s an affordable way for small businesses that do not have an IT team to handle ecommerce.
Main Features of Ecommerce Websites
There are a few features your website should include for ecommerce functionality. Tailor your ecommerce website to include:
- User-Friendly Features: When people shop online, they want to quickly and easily find whatever they are looking for.
- Easy Navigation: Clear navigation menus that make it easy to browse products by category. Place the menus in an easy-to-find place, either on the side of the page or across the top. Keep them consistent across every page.
- Product Filters- Product filters so that shoppers can sort through product offerings to find what they want quickly. For example, allow customers to filter by price, size, color, product type, brand, style, etc
- Product Availability- Include product availability information for each of your products in a prominent location on the product page. If any products do go out of stock, have information about when you can expect them to be available again.
- Clear Cart and Checkout Buttons: To encourage conversions and higher online transaction volume, make sure your “add to cart”/ “buy now” buttons, and checkout buttons are clear. When a customer clicks to visit their cart, make sure they can see all the essential details such as: Item names, Price, Product quantity. Make it quick and easy to remove items or change the quantity from within the cart page. Most importantly, allow your customers to save their cart and come back to it later.
- Multiple Payment Options: The more payment options you offer, the better it is for you and your customer experience. This way, they have the flexibility to use their chosen payment method and can place their order in just a few clicks. Popular options include:
- PayPal
- Google Pay
- Apple Pay
- Amazon Pay
- Credit or Debit cards
- Customer Service and Contact Options: Your customers need to be able to reach you with questions and concerns about their orders. If you’re not ready to invest in online support ticketing tools or live chat, you should at the very least have:
- A dedicated email address that’s prominently displayed
- Links to your social media accounts so people can reach you there
- Self-service options to make it easy for customers to initiate a return or exchange request
- Company phone number and address in the footer
Important Website Content
Your potential customers will have questions. Make certain information easy to find.
Order Processing Timeline
How long does it take you to pack and ship an order after it is placed? Give an estimate but allow yourself plenty of time to process the order. Most companies ship orders within 1 to 5 business days from the date of the order.
Do orders placed before a specific time of day get shipped the same day? If so, make sure that time is clearly displayed.
Shipping Policies
What does your standard shipping look like? Do you offer expedited shipping? What carriers do you use? Do you ship internationally? Do you cover return shipping costs?
Return Policies
Do you accept product returns? If so, what are the terms? 30 days? 60 days? Is money refunded or store credit offered? Spell out these policies to help guide people in their shopping choices.
Privacy Policy
Store owners are legally required to have a privacy policy on their ecommerce site. This document outlines how your ecommerce business will collect, store, protect, and use any personal information internet users provide. This includes information such as:
- Name
- Date of birth
- Addresses (Email, physical, and shipping)
- Payment details
- Location (IP address, geolocation, etc.)
Terms of Service
In addition to a privacy policy, your e-commerce site plan should also have a Terms of Service page. It’s what sets the rules for your using website.
The terms and conditions of your website can limit liability if a customer decides to take you to court. Plus, it can help protect your rights to the content on your website.
If you ever find yourself in a legal battle, the court will look at your terms and conditions to determine the contract between you and the customer. If you want it to hold up in court, you may want to have a legal team handle this too.
Do not copy the terms and conditions of another site. You can use sites similar to yours to help guide you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Always include a frequently asked questions page where customers can find the answers they’re looking for.
Mobile-Friendly Website
A responsive design automatically adjusts your website’s core features – navigation, images, buttons, etc. so that it fits comfortably on a smartphone or tablet screen. Failure to account for this will hurt your ecommerce website since Google considers this a ranking factor. If it’s not mobile optimized, your website won’t rank as high in the search engine, no matter how well you’re doing with your other marketing efforts.
User Ratings and Reviews
Add user ratings and reviews to as many of your products as you can. User-generated reviews are read and appreciated by online shoppers.
High-Quality Photos
High-resolution images are great, but their large file size can dramatically slow down your website speed. That’s why you should start with a web-optimized version and allow your customers to click to see the full image.
High-Quality Videos
Whenever possible, use video to demonstrate your products. This is helpful for products that people want to see and feel before they buy. If a photo is worth 1,000 words, imagine the impact of video.
Trust Symbols
Your ecommerce website, especially when it is new, needs to have plenty of trust symbols. Until customers become familiar with your brand, these symbols will help foster a connection. Trust badges legitimize your website. Research shows that 98% of consumers surveyed found at least one type of trust signal that increased their purchase likelihood.
Guaranteed Safe and Secure Checkout
This helps reinforce your website’s security to help customers know their payment information is safe.
Free Shipping and Free Returns
Of course, you should only use this badge if you offer both free shipping and free returns. If not, it will be false advertising and upset your customers.
Accepted Payment Badges
This is a quick and easy way to show all the payment methods you accept so that people can choose their preferred payment method. These trusted brand names will help you establish trust with your audience.
Third-Party Endorsements
If you have any third-party endorsements, such as a Better Business Bureau accreditation or Google Reviews, add these to your website.
Coupons and Special Offers
Customers adore special offers. Use email marketing and social media to provide exclusive coupons and special offers to those already engaged with your brand. Offer a percent discount, free shipping at a certain threshold, or another limited-time offer.
Upselling and Cross-Selling
To increase sales, offer customers the option to get a better price when they buy more. Upselling happens when you raise a customer’s order value by offering additional services or encouraging them to purchase an upgraded product or service.
Alternatively, you can use cross-selling, which is when you add offers of items that either supplement or complement your customer’s purchase. For instance, if a customer purchases a phone case, you can cross-sell screen protectors, chargers, and other accessories.
Wishlist
If you have a lot of products, consider adding a wish list function to your site. This will allow your customers to make a list of things they’d like to order from you. Plus, they can share that list with friends and loved ones to make gift-giving easier.
